What is a good quality pbr fabric material
Learn how to create realistic PBR materials using high-resolution maps that control color, light, and surface details for true-to-life results.
How to define a good quality PBR material.
A good PBR material accurately simulates real-world light behavior using calibrated texture maps for color, reflection, and surface detail.
Each map—albedo, normal, roughness, metalness, and displacement—must be physically consistent, high-resolution, and correctly aligned with the rest of the Textures maps.
True quality appears when the material responds realistically under any lighting setup, showing balanced highlights, micro-surface variation, and no baked-in shadows.
Before PBR, 3D graphics often looked flat and unrealistic. Physically Based Rendering revolutionized digital visuals by using real-world physics and mathematical models to simulate how light truly interacts with different materials.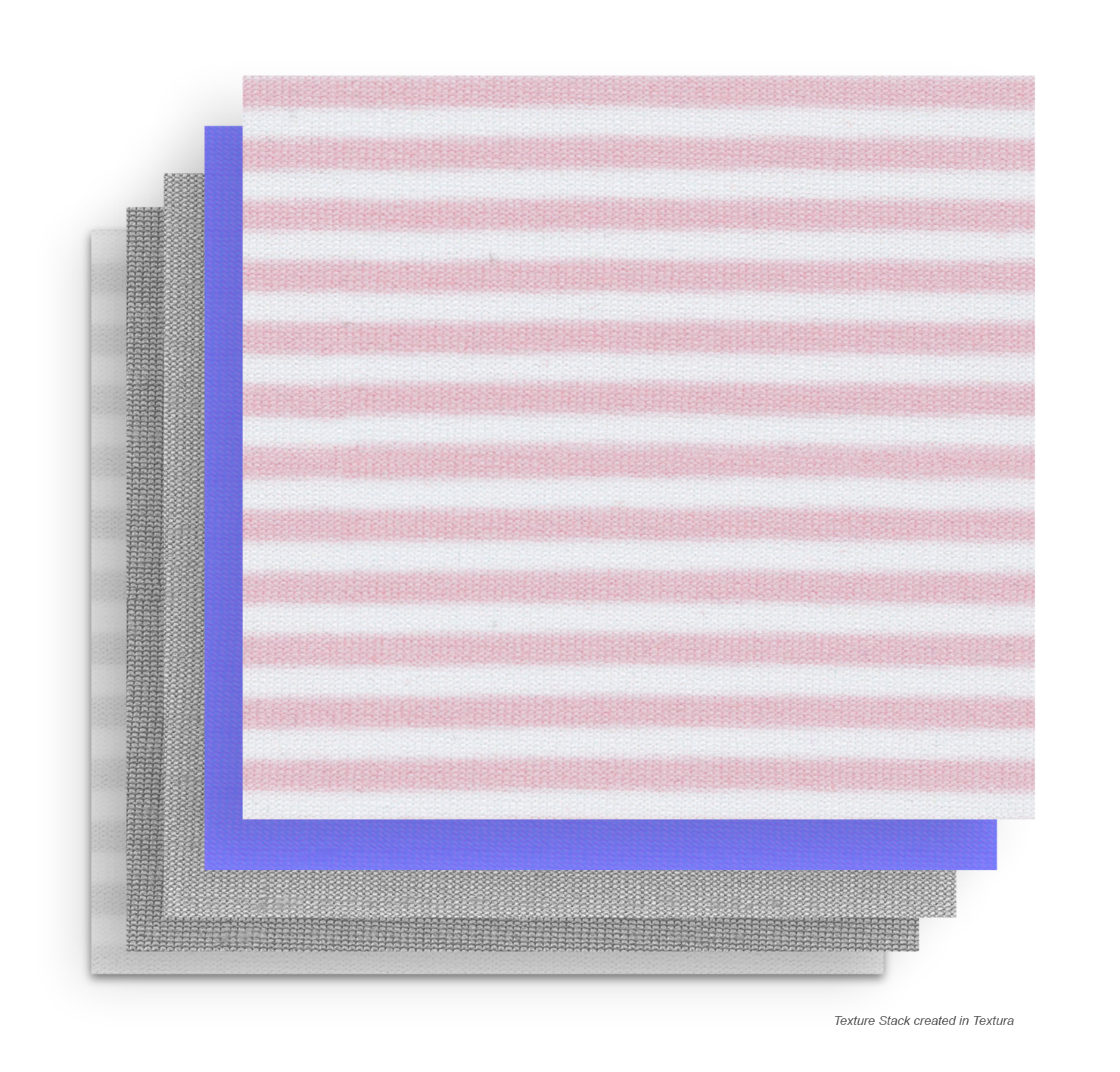
A professional PBR material usually includes 5–6 essential texture maps, all perfectly aligned (same UV scale, same naming, same resolution):
Texture maps contain the essential data needed to replicate real physical surface properties.
In Textura, the texture stack includes maps, physics, and metadata—the core components that define every PBR material.
Albedo Map,
also referred to as a diffuse map in other software.
• What it is: The base color or diffuse texture of your material.
• What it controls: The overall color and pattern seen on the surface — without lighting or reflection information.
This is the scan as is, right from the scanner, your base image.
Specular Map
What it is: Defines how shiny the surface is and how much light is reflected.
White areas: Strong reflection; black areas: matte finish.
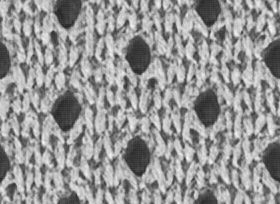
Roughness Map
• What it is: Defines how rough or smooth a surface is.
• White = rough (diffused reflections), black = smooth (mirror-like reflections).

Roughness indicates how smooth or rough the surface of an object is.
Low roughness generates a more reflective surface and high roughness a diffuse one.
Alpha Map
• What it is: Controls the transparency of the material.
• White = opaque, black = fully transparent.
• Used for: Cutouts (like lace holes, glass transparency, or fabric mesh).

The Alpha Map defines which areas are partially or totally transparent, and which ones are fully opaque.
Normal Map

A normal map simulates the illusion of surface details. Alters the direction of the incident light, generating shadows.
• What it is: A map that simulates small surface details (bumps, wrinkles, stitches) without changing geometry.
• How it works: Alters how light interacts with the surface to fake depth and relief.
• File type: Usually bluish-purple images (tangent-space normal).
Example: Creates the illusion of embroidery or a woven texture on a flat surface.
Displacement Map
Displacement simulates additional geometric details, altering the geometry by “moving” the polygons.
• What it is: Modifies the mesh geometry based on height values.
• White areas: Move outward (high); black areas: stay low.
• Requires more render time and geometry. Off-Line Render.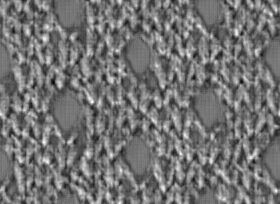
Other Maps
Other maps can produce more complex visual effects for a material, such as Bump, transmittance, metalness, or sheen.
By default, Textura doesn't generate the Metallic map, but you can get it through the "Edit Material" section, by selecting a metallic or satin preset, and running the maps again.
A metallic map will be added to the fabric texture maps set upon this request.
Do you prefer to watch a video? Check Textura's YouTube channel here:
